
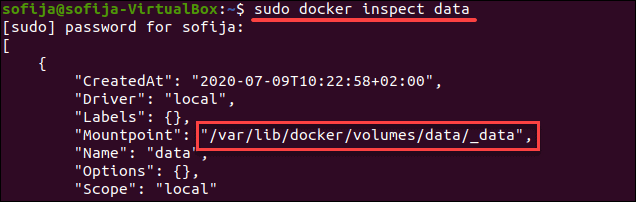
Open up the one for the container you want to modify. In here will be many folders cooresponding to Docker container IDs, which you can find with docker ps. You’ll need to navigate to Docker’s storage directory: cd /var/lib/docker/containers Of course, this is far more complicated than just dealing with a container restart, so if you can manage a minute of downtime, we highly recommend doing that instead. Because of this, you can actually modify that configuration directly, and restart the entire Docker daemon for your system to apply those changes without restarting at all. docker run -d \ĭocker volumes are really just trickery that the Docker runtime uses to expose host directories to containers, and it all depends on configuration. Then, you can run the new image, replacing the old image with the cloned one. Grab the container ID from docker ps: docker psĪnd then, clone it with commit: docker commit f88f33c918d2 imagename But, if you do need to add a volume to a running container, you can use docker commit to make a new image based on that container, and then clone it with the new volume. This method probably isn’t a good idea for most people, as it requires you to make a new image every time you want to do this, and it still requires downtime. Anything that you care about, such as application data, should be stored in a volume so that it can be persisted across container restarts and rebuilds. In almost all cases, you shouldn’t be depending on a container’s current running state. RELATED: What Is Docker Compose, and How Do You Use It? Cloning From An Existing Container You can also manually run docker-compose down beforehand to stop the services, but it isn’t necessary in most cases unless you want to run it with the -v flag to destroy existing volumes.
#Docker run image with volume update
If you want to update the images, you’ll need to run docker-compose up with the -build flag: docker-compose up -d -build
Compose has a “restart” command, but it’s actually to just refresh the running service without any config changes. Then, you can restart Docker Compose’s services. you’ll need to add the volume to the docker-compose.yml file: version: "3.0" If you’re using Docker Compose, you can automate and track this process more easily, since the volume configuration is handled through a settings file. mount source=nginx-config,target=/etc/nginx \ If you want to add a volume, you’ll need to stop the running container: docker stop my_containerĬreate a new volume if you need to: docker volume create nginx-configĪnd then run it with an updated launch command, adding the -mount flag to configure the source volume and target destination.
#Docker run image with volume code
Modern auto-scaling systems should be designed to handle that, as code deployments happen often. If your service is big enough that you are concerned about a few minutes (at most) of potential scheduled downtime to restart the container, you should probably be running a scaling deployment with multiple instances that can be updated independently. Having updates tracked in Git is another big factor, especially if you’re using Docker Compose, and editing the launch script is far better than manually adding the volume to a running container.
Restarting the container is fairly easy, and most code updates require a restart of the service anyway. While there is a hacky solution (more on that below), it’s highly recommended that a container restart should be done anyway. Containers must have their volumes configured on startup, which means to add a new volume, you must restart the container. Unfortunately it’s not as simple as just adding a new volume. Usually, you add volumes to containers in the creation script, but what if you need to make new ones? Adding a Volume To a Running Docker Container While Docker is a useful tool for packaging and managing applications, it also presents many unique challenges, such as dealing with stored data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
